USING JUMPSTART IN TOMCAT 5.5 OR 6.0
Tomcat 7.0 support may be possible when OpenEJB updates their Tomcat installer, openejb.war. ContentsPrepare Tomcat
Build and deploy JumpStart
Build, deploy, and integration test JumpStart
Use JumpStart
How to run integration tests from Eclipse
How to debug the client side
How to debug the server side
Prepare Tomcat
These instructions prepare Tomcat with the following elements:
| Web Server | Business Server | Persistence | Database Server | Logger |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tomcat | OpenEJB3 | Hibernate | HSQLDB | Log4j |
| (Added by us) | (Added by us) | (Tomcat's default) | (Added by us) |
- Start by doing a Tomcat Installation - those instructions work just fine for 5.5, not just "6.x".
- Then install the OpenEJB plugin:
- Go to Apache Download Mirrors and download openejb.war (OpenEJB 3.1.4 for Tomcat).
- Move openejb.war to ${catalina.base}/webapps/ (Note: the file must be named openejb.war)
- Start Tomcat if it is not already running, eg.
...in Windows:- cd /devel/apache-tomcat-6.0.n/bin
- startup.bat
- cd /devel/apache-tomcat-6.0.n/bin
- ./startup.sh
- Visit http://localhost:8080/openejb/installer and click the 'install' button.
- Stop Tomcat, eg.
...in Windows:- cd /devel/apache-tomcat-6.0.n/bin
- shutdown.bat
- cd /devel/apache-tomcat-6.0.n/bin
- ./shutdown.sh
- Add Hibernate to Tomcat:
- Open the JumpStart project's data_util.properties file and modify the property add.hibernate.to.dir eg. to ../apache-tomcat-5.5.n/common/lib or ../apache-tomcat-6.0.n/lib .
- Drag data_util.xml to the Ant view and run its target add-hibernate-to-a-server.
- If using Tomcat 5.5...
- Check Tomcat's common/lib/ now has the Hibernate jars, eg. hibernate-core-n.n.n.jar.
- If using Tomcat 6.0...
- Check Tomcat's lib/ now has the Hibernate jars, eg. hibernate-core-n.n.n.jar.
- Add log4j and jndi config.
- If using Tomcat 5.5...
- From business/src/main/resources/conf-log4j-tomcat5.5/, copy log4j.properties to Tomcat's common/classes/.
- From business/src/main/resources/conf-jndi-tomcat-openejb/, copy jndi.properties to Tomcat's common/classes/.
- If using Tomcat 6.0...
- From business/src/main/resources/conf-log4j-server-side/, copy log4j.properties to Tomcat's lib/.
- From business/src/main/resources/conf-jndi-tomcat-openejb/, copy jndi.properties to Tomcat's lib/.
- If using Tomcat 5.5...
- Set JVM options:
- Here are some JVM options to consider:
-Dhibernate.hbm2ddl.auto=update ESSENTIAL for JumpStart initially. Great during development, but
NOT RECOMMENDED IN A PRODUCTION ENVIRONMENT because data can be lost. Tells Hibernate to automatically bring the database structure into line with the app's entity definitions at every restart. See hibernate optional configuration properties.-Dtapestry.production-mode=false Tells the Tapestry ExceptionReport page to display full details of the exception, which is great during development. When set to true (which is the default since T5.0.10), Tapestry's ExceptionReport page will display an abbreviated report so as to avoid disclosing details of your application's internals. See Configuring Tapestry. -Dtapestry.compress-whitespace=false Tells Tapestry not to compress whitespace as it generates a page from a template. Makes the generated page source much easier to read eg. when you tell your browser to display the page source. See Configuring Tapestry. -Xms256m -Xmx256m Gives Tomcat more memory for its heap, avoiding "out of memory" errors. -XX:MaxNewSize=96m -XX:MaxPermSize=96m Gives Tomcat more Perm Gen memory. If you encounter Perm Gen memory errors as you make mods to the app then consider raising this higher.. - You can set them from the command line:
...eg. in Windows:- set CATALINA_OPTS=-Dhibernate.hbm2ddl.auto=update -Dtapestry.production-mode=false -Dtapestry.compress-whitespace=false -Xms256m -Xmx256m -XX:MaxNewSize=96m -XX:MaxPermSize=96m
- setenv CATALINA_OPTS "-Dhibernate.hbm2ddl.auto=update -Dtapestry.production-mode=false -Dtapestry.compress-whitespace=false -Xms256m -Xmx256m -XX:MaxNewSize=96m -XX:MaxPermSize=96m"
- Here are some JVM options to consider:
- Start Tomcat, eg. from the command line like this:
...in Windows:- cd /devel/apache-tomcat-6.0.n/bin
- startup.bat
- cd /devel/apache-tomcat-6.0.n/bin
- ./startup.sh
- Set the build properties: in the JumpStart project's build.properties file, edit the value of these properties:
- deployment.server.type
- deployment.persistence.descriptor
- deployment.web.descriptor
- deployment.server.dir
Build and deploy JumpStart
Here we use Ant to clean, compile, unit test, package, deploy to the server, and wait for it to load.
The deployed package is jumpstart.war.
- In Eclipse, drag build.xml to the Ant view and run its target clean-compile-test-package-deploytoserver-checkactive.
- If you get an error about JAVA_HOME, read this. Use a JDK 1.6 tools.jar.
Build and deploy and integration test JumpStart
Here we use Ant to clean, compile, unit test, package, deploy to the server, wait for it to load, and run the business integration test suite.
The deployed package is jumpstart.war. The tests remotely call the JumpStart business layer services exposed by the server.
- In Eclipse, drag build.xml to the Ant view and run its target clean-compile-test-package-deploytoserver-integrationtest.
- If you get an error about JAVA_HOME, read this. Use a JDK 1.6 tools.jar.
Use JumpStart
Ensure the command line is using Java 1.6: the commands java -version and javac -version must return a variant of 1.6, eg. 1.6.0_13.
Start Tomcat (as above).
Confirm Tomcat is using Java 1.6: when you start Tomcat it returns 4 messages, with the last one giving the JRE_HOME path.
The JRE_HOME must be a Java 1.6 JRE or JDK. If it is Java 1.5 or earlier, then shut down Tomcat and fix this before proceeding.
Before you use JumpStart for the first time in a new server, you need to build it, deploy it, and run an integration test.
Stop Tomcat (as above).
Populate the Hypersonic database (HSQLDB) within Tomcat: in Eclipse...
- Open the data_util.properties file and modify the property hsqldb.data.dir.
Use relative paths eg. ../apache-tomcat-6.0.n/data/hsqldb . - With the data_util.xml file in the Ant view, run its target reset-database-hsqldb-prompted.
It will prompt you to confirm.
If you get the error "Cannot load 32-bit SWT libraries on 64-bit JVM", then right-click on the target reset-database-hsqldb and choose Run As > Ant Build... > JRE and change the Runtime JRE from 1.6 (or similar) to 1.5 (or similar), and click Run.
When the server is running you can visit JumpStart with your web browser at http://yourserver:8080/jumpstart.
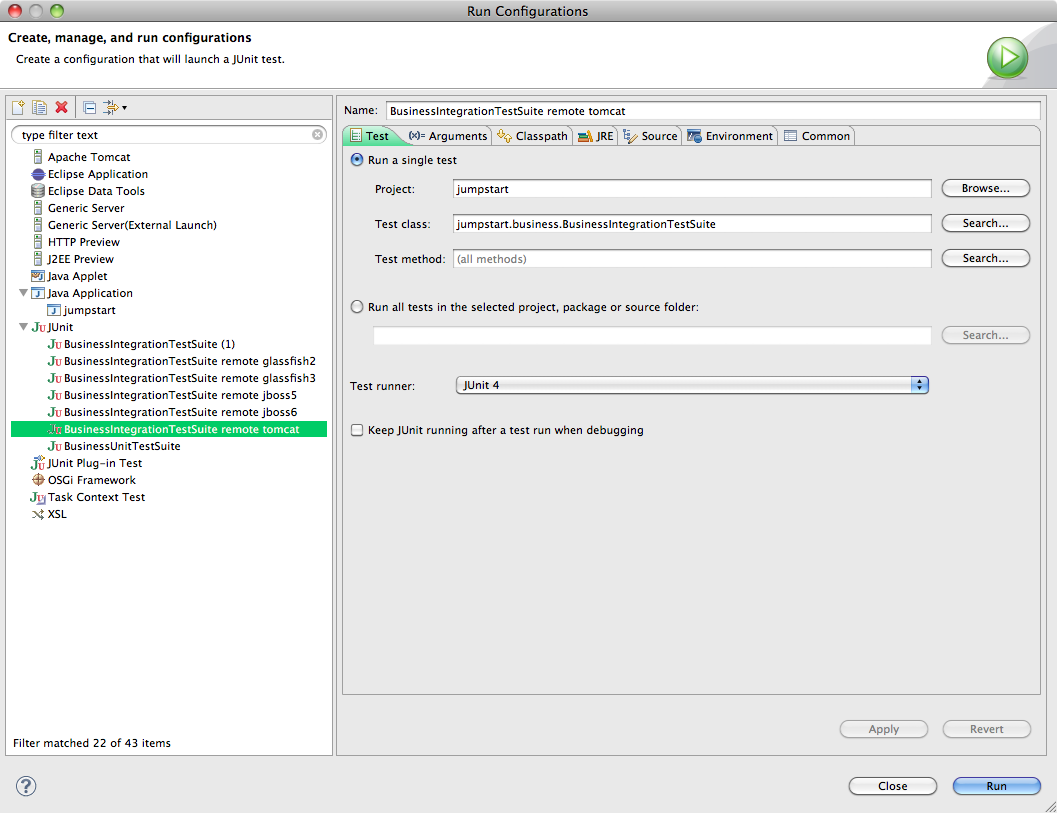
How to run integration tests from Eclipse
First, build and deploy JumpStart as described above.
Second, create a User Library over Tomcat:
- In Eclipse, choose Window > Preferences > Java > Build Path > User Libraries (or in OS X, choose Eclipse > Preferences > Java > Build Path > User Libraries), and
- Create a new user library called tomcat-5.5-client-lib or tomcat-6.0-client-lib, then
- Add Tomcat's webapps/openejb/lib/openejb-client-3.1.4.jar file to the new user library.
|
|
|
|
- Click Run.
- Watch the results in the JUnit View panel. In the Console View you might see lots of exceptions but that's normal. The JUnit View will tell you quickly whether the tests succeeded or not.
- Problems? Eclipse might not be ready for junit - see Could not create task or type of type: junit.
How to debug the client side
To debug, for example, the client side of the integration tests, use Run > Debug Configurations... instead of Run > Run Configurations....
Eclipse will then stop at breakpoints, display variables, enable single-stepping, etc. in the test suite.
How to debug the server side
To debug any part of JumpStart as it runs in the server you'll need to be running Tomcat in debug mode. There are a couple of ways to do it:
- Start Tomcat in debug mode
We'll use port 8787 in this explanation, but it's OK to use any free port.
Earlier, we described setting various JVM options. To run Tomcat in debug, include these JVM options:
-
-Xdebug -Xrunjdwp:transport=dt_socket,address=8787,server=y,suspend=y
-
Listening for transport dt_socket at address: 8787
In Eclipse, right-click on your project and choose Debug As > Debug Configurations... and the Debug Configurations window will appear.
- Right-click on Remote Java Application and choose New.
- Set the Port to 8787.
- Enable Allow termination of remote VM.
- Click on Debug.
Tomcat resumes startup, and Eclipse will now stop at breakpoints, display variables, do single-stepping, etc. on any Java in the project.
- Control Tomcat server from Eclipse
In Eclipse's Server view, add your Apache Tomcat 5.5 or 6.0 server.
You can set the JVM options, as described above, by right-clicking on the server entry and choosing Open > Open launch configuration > Arguments.
You can start the server by right-clicking on the server entry and choosing Start or Debug.